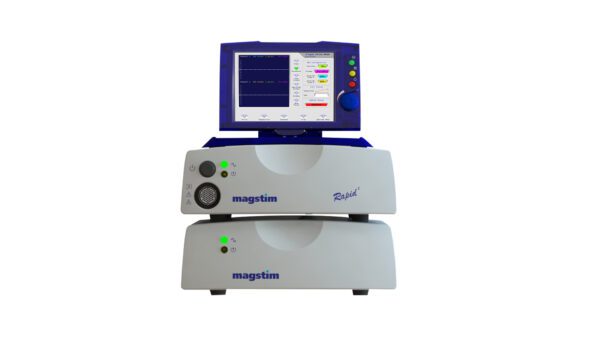
Rapid²
This Rapid² System features a single HV Power Supply Unit (PSU) (3KVA).
Magstim Rapid² stimulators have been used in numerous fundamental and clinical research studies worldwide, offering performance capabilities to meet a variety of research requirements, and compatible with a wide range of Magstim coils.
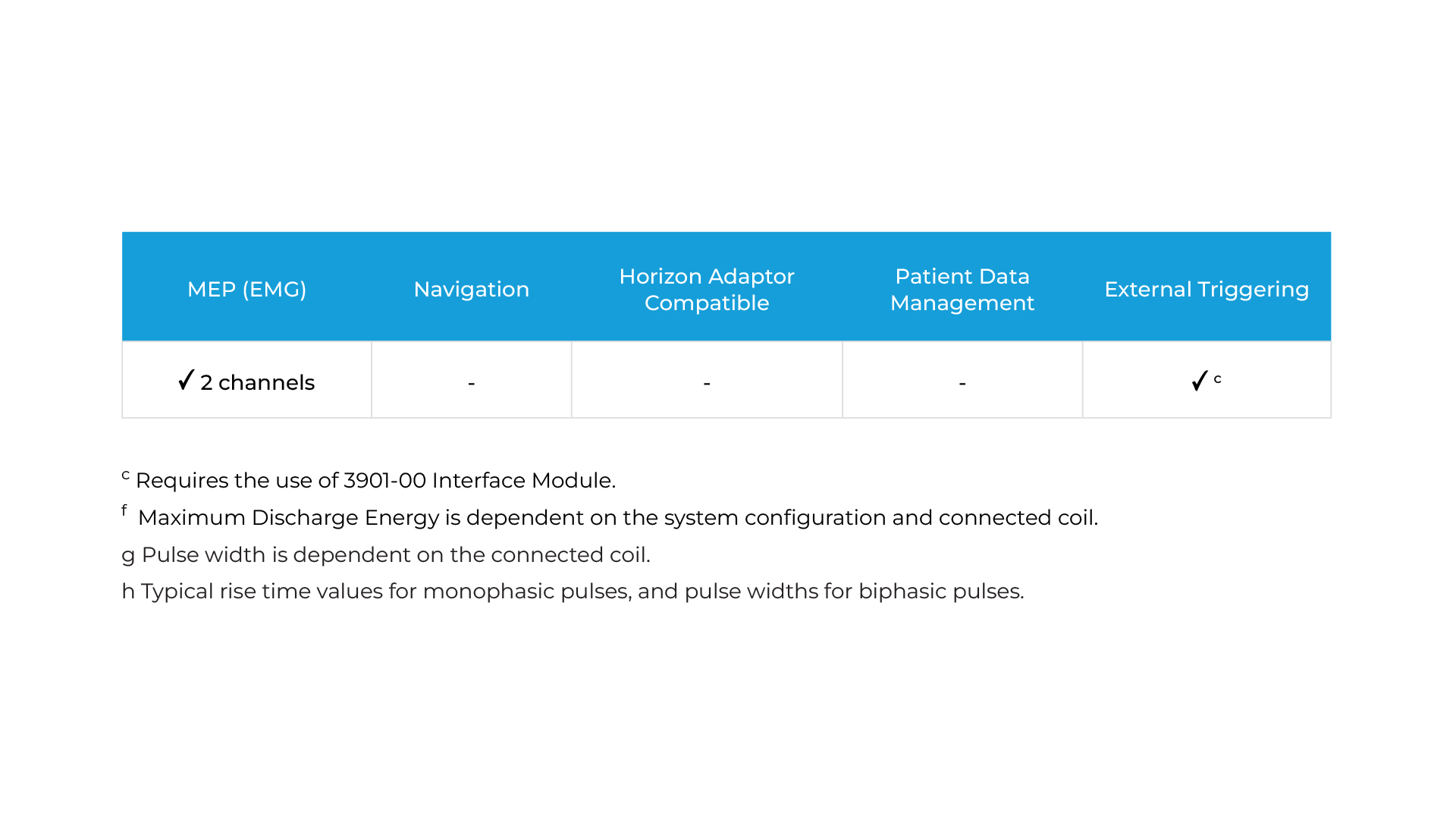
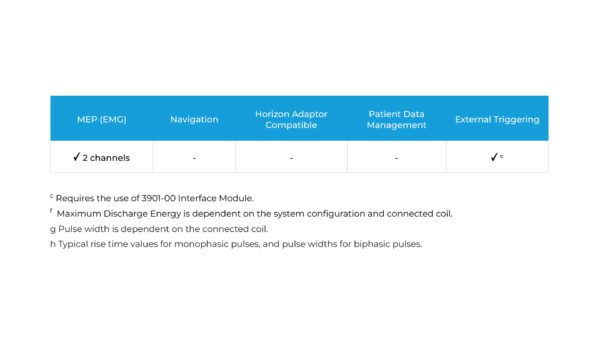
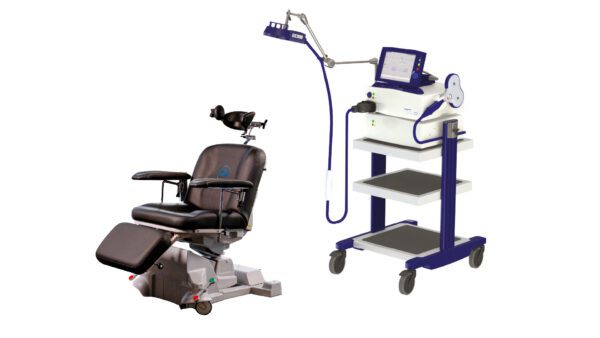
Capable of high-frequency and theta burst stimulation protocols for both cortical and peripheral research applications. Integrated display of motor evoked potentials (MEPs)*, with charge delay function for reduced artifacts during MEP or EEG recording. A Magstim Interface Module permits simple integration with external triggering and recording devices. The Rapid² Series stimulator comes in three variants of power capability to meet the needs of every application.
Ideal for a wide range of fundamental and clinical research applications applying neural modulation.
Suitable for both cortical and peripheral stimulation.
c Requires the use of 3901-00 Interface Module.
Contact Us
Contact us